Programming Assignment 1: Playing with Sound
- Due Date:
2/22/20172/24/2017
Sound
Sound waves are compressions of air.
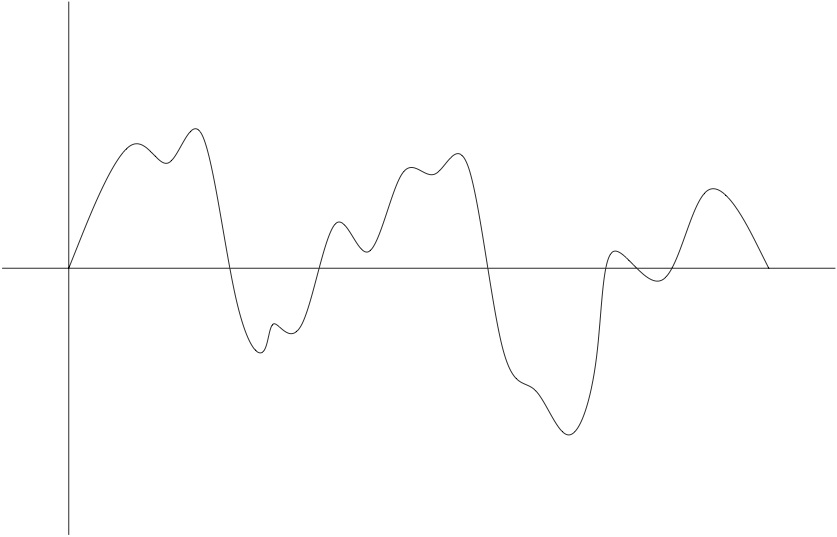
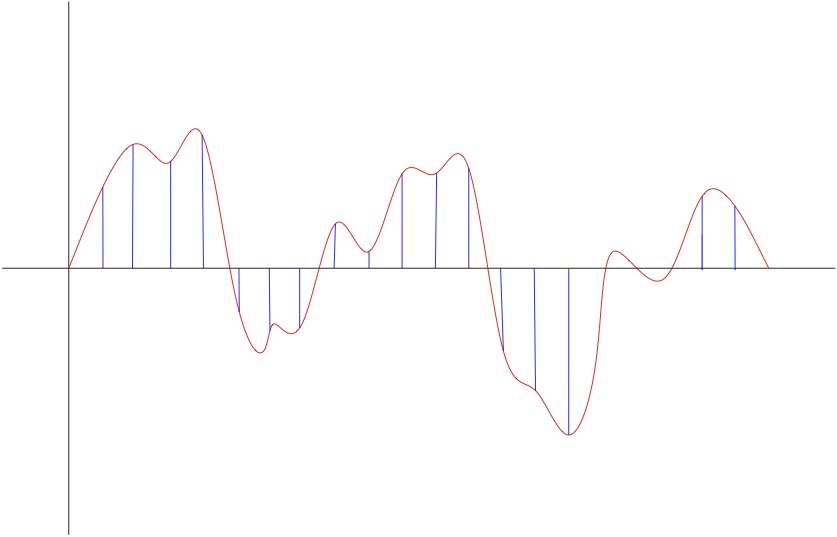
Sound waves are an inherently analog phenomena, to represent them in a digital domain, we need to sample them. We choose a sampling rate (say, 10000 samples a second) and then every 1/1000th of a second, we record the value of the wave at that point. We then save all of these samples, and that is our internal representaion of the sound.
Sometimes we want to record multiple channels of sound. For instance, stereo headphones have 2 separate channels of sound (one for the left ear, and one for the right). Surround sound systems can have even more channels -- 5.1 has 6 channels: Front-Left, center, Front-Right, back-left, back-right, subwoofer.
Linked Lists
For the first project, You will implement a data structure that stores and manipulates sound clips using a linked-list structure. Speficially, sounds will be stored as a linked list of samples, where each sample is a linked list of the sampled values for each channel. For example, a SoundList for a 3-channel sound containing 4 samples would look something like the following:
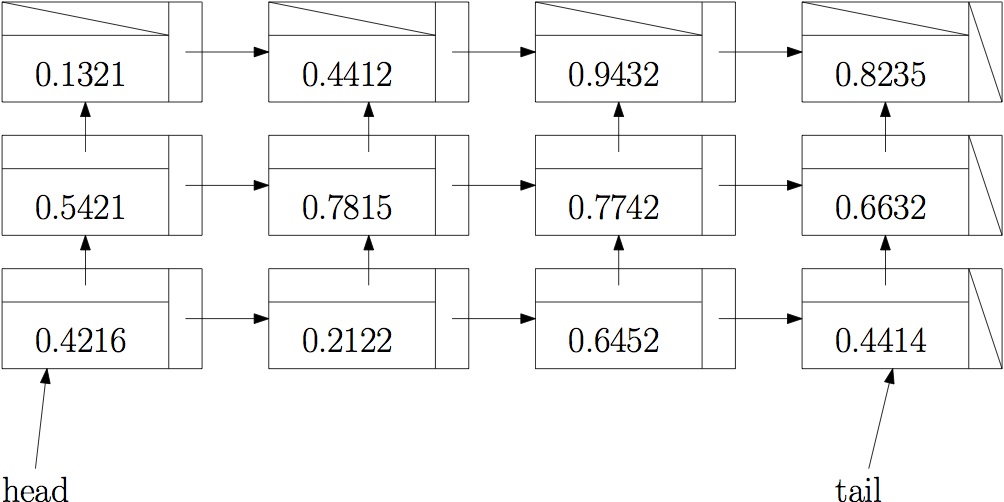
Note that your are
But ... But ...
I can already hear you saying:
- But arrays woould be more effiient!
- But using ArrayLists is much easiear!
- But in the real world we will use libraries!
All valid points, however:
- The point of this assignment is to get comfortable with linked lists. I tried to come up with a compelling application, but the point is to learn to manipulate linked structures, not to create the best possible implemenation of a sound library.
- In this instance, easier is not better -- remember that the point is to learn how to use somewhat complicated linked structures.
- Before you can use libraries effectively, you need to know exactly how they are implemented (that is sort of the point of this class!) Be glad I have not given you an assignmment that cannot easily use the Java libraries! (Yes, such problems exist! I have needed to solve them in the wild. They are also very. very difficult. Fun, but difficult!)
Implementation
You will implement the following interface:SoundList.java
import java.util.Iterator;
public interface SoundList {
/**
* The number of channels in the SoundList
* @return The number f channels in the SoundList
*/
public int getNumChannels();
/**
* Returns the sample rate, in samples per second
* @return The sample rate, in samples per second
*/
public float getSampleRate();
/**
* Returns the number of samples in the SoundList
* @return The number of samples in the SoundList.
*/
public int getNumSamples();
/**
* Returns The duration of the sound, in seconds.
* @return the duration of the sound, in seconds.
*/
public float getDuration();
/**
* Fade in. Smoothly ramp the volume up for fadeDuration sections.
* @param fadeDuration The time (in seconds) to fade in.
*/
public void fadeIn(float fadeDuration);
/**
* Fade out. Smoothly ramp the volume down for fadeDuration sections.
* @param fadeDuration The time (in seconds) to fade in.
*/
public void fadeOut(float fadeDuration, float startTime);
/**
* Remove the silence at the front and back of the clip. All samples at the beginning of the clip
* whose absolute value is less than or equal to maxLevel are removed, until a sample whose absolute value
* is that is > maxLevel appears. Then retain all samples until the end, at which point all samples
* whose absolute value is <= maxLevel are removed.
* Note that a value > maxLevel on any channel is sufficient to keep the sample.
* @param maxLevel The level at which the sample is kept.
*/
public void trimSilence(float maxLevel);
/**
* Add an echo effect to the SoundList.
* @param delay The time (in seconds) before the echo starts
* @param percent The percent falloff of the echo (0.5 is 50 percent volume, 0.25 is
* 25 percent volume, and so on. All samples should be clipped to the range -1 .. 1
*/
public void addEcho(float delay, float percent);
/**
* Reverse the SoundList.
*/
public void reverse();
/**
* Change the speed of the sound.
* @param percentChange How much to change the speed. 1.0 is no change, 2.0 doubles the speed (and the pitch), 0.5
* cuts the speed in half (and lowers the pitch) The sample rate should remain unchanged! This is probably the hardest
* function to implement in the entire project.
*/
public void changeSpeed(float percentChange);
/**
* Add a single sample to the end of the SoundList. Throws an exception if the soundlist has more than 1 channel
* @param sample The sample to add
*/
public void addSample(float sample);
/**
* Adds a single sample for each channel to the end of the SoundList. Throws an exception if the size of the sample
* array is not the same as the number of channels in the sound list
* @param sample Array of samples (one for each channel) to add to the end of the SoundList
*/
public void addSample(float sample[]);
/**
* Return an iterator that traverses the entire sample, returning an array floats (one for each channel)
* @return iterator
*/
public Iterator iterator();
/**
* Change the volume of all tracks in the sound list, by multiplying every value by the percent to change.
* If allowClipping is true, values greater than 1.0 are set to 1.0, and values less than -1.0 are set to -1.0
* If allowClipping is false, then if any values are greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 in any clip, the entire sample
* is rescaled to fit in the range.
* @param percentToChange The percent to increase the volume. A value of 1 will leave the clip unchanged, 2.0
* will make the volume twice as loud, and 0.5 will make the volume 50% as loud.
* @param allowClipping If allowClipping is true, then values greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 after the
* volume change are clipped to fit in the range. If allowClipping is false, then if any values are greater than 1.0
* or less than -1.0, the entire sample is rescaled to fit in the range.
*/
public void changeVolume(float percentToChange, boolean allowClipping);
/**
* Return an iterator that traverses a single channel of the list
* @param channel The channel to traverse
* @return the iterator to traverse the list
*/
public Iterator iterator(int channel);
/**
* Trim the SoundList, by removing all samples before the startTime, and all samples past the end time.
* Note that if a SoundList represents an 8 second sound, and we call clip(4,7), the new SoundList will be
* a 3-second sound (from seconds 4-7 in the old SoundList)
* @param startTime Time to start (in seconds)
* @param endTime Time to end clip (as measured from the front of the original clip, in seconds)
*/
public void clip(float startTime, float endTime);
/**
* Splice a new SoundList into this soundList. Both SoundLists will be modified. If the sampleRate of the
* clipToSplice is not the same as this SoundList, an exception is thrown.
* @param startSpliceTime Time to start the splice
* @param clipToSplice The other SoundClip to splice in.
*/
public void spliceIn(float startSpliceTime, SoundList clipToSplice);
/**
* Combine all channels into a single channel, by adding together all channels into a single channel.
* @param allowClipping If allowClipping is true, then values greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 after the
* addition are clipped to fit in the range. If allowClipping is false, then if any values are greater than 1.0
* or less than -1.0, the entire sample is rescaled to fit in the range.
*/
public void makeMono(boolean allowClipping);
/**
* Combines this SoundList with a new SoundList, by adding the samples together. This SoundList
* is modified. If the sampleRate of the clipTocombine is not the same as this SoundList, an exception is thrown.
* If a SoundList of length 3 seconds and a SoundList of length 7 seconds are combined, the result will be a
* SoundList of 7 seconds.
* @param clipToCombine The clip to combine with this clip
* @param allowClipping If allowClipping is true, then values greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 after the
* addition are clipped to fit in the range. If allowClipping is false, then the entire sample is rescaled
*/
public void combine(SoundList clipToCombine, boolean allowClipping);
/**
* Returns a clone of this SoundList
* @return The cloned SoundList
*/
public SoundList clone();
}
Where:
- getSampleRate Returns the sample rate of this sound clip. This one is easy, you just need to return the sampleRate that was used when the SoundList was created
- getNumSamples Returns the number of samples in the list. This should be stored (and not recalculated each time getNumSamples is called)
- getDuration Returns the duration of the clip, in seconds. Relatively easy to compute given the number of samples and the sample rate
- addEcho Adds an echo effect to the soundList
- reverse Reverses the list of samples. Helpful for finding backmasked messages, like Paul is dead
- changeSpeed(float percentChange) Change the speed of the SoundList. A percentChange of 1.0 leaves the sound unchanged, while 2.0 makes the clip twice as fast (also twice as high!) This is the hardest method!
- addSample(float sample) Adds a sample to the end of the SoundList. If the SoundList is not single-channel, thiis method should throw and IllegalArgument exception
- addSample(float sample[]) Adds a sample to the end of the SoundList. If the length of the sample array is not the same as the number of channels in the SampleList, throw an IllegalArgument exception
- Iterator<float[]> iterator() Returns an iterator to traverse the SoundList. Each call to next returns an array of samples, one for each channel
- Iterator<Float> iterator(int channel) Returns an iterator to traverse a single channel of the SoundList
- clip(float startTime, float duration) Clips the SoundList by throwing away all samples before the startTime (in secounds), and after the duration (in seconds). So, if the SoundList was 6 seconds long, and we called clip(4,2), the new SoundList would be 2 seconds long (and would consist of samples from second 4 to second 6 of the original SoundList)
- spliceIn(float startSpliceTime, SoundList clipToSplice) Splice clipToSplice into this clip, starting at startSpliceTime
- combine(SoundList clipToCombine, boolean allowClipping) Add the waveform of clipToCombine to this clip. If allowClipping is true, clip all samples in the range -1, 1. If allowClipping is false, rescale resuting waveform to be in the range -1, 1
- public void makeMono(boolean allowClipping); Combine all channels into one. If allowClipping is true, clip all samples in the range -1, 1. If allowClipping is false, rescale resuting waveform to be in the range -1, 1
- public void fadeIn(float time); Fade in for time seconds. The fade in should be linear.
- public void fadeOut(float startTime, float duration); Fade out starting at startTime. The fade out should last for duration seconds.
- SoundList clone() Return a clone (deep copy) of the SoundList
- public void trimSilence(float maxLevel) Remove the silence at the front and back of the sample